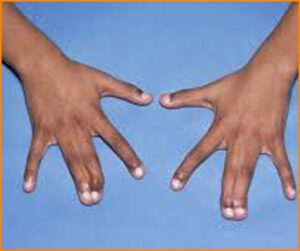
The Syndactyly Misconfiguration
It is one of the most common forms of congenital malformation of the limbs and it is commonly characterized by abnormal connection of fingers of the hand which appears to be webbed together. The male is likely to get more prone to this defect when compared to females as per the demographic data.
The diagnosis of this defect is made clinically when the child’s age is around 6 to 12 months.
Epidemiology Of This Misconfiguration
It is a very common defect as the chances of its occurrence in infants is 1 in 2000 but thanks to our advanced medical technology which allows it to be treated efficiently with no side effects.
Etiology Of The Syndactyly
There are many causes that can lead to syndactyly in which the major reasons are associated with genetics, various syndromes and bad pathophysiology.
Due To Bad Pathophysiology
It is perhaps the most common reason which led to syndactyly misconfiguration. It is caused mainly due to the failure of apoptosis to separate digits which ultimately leads to the syndactyly disorder.
Genetic Reasons
Genetics also plays a vital role in determining the extent and severity of the syndactyly misconfiguration. This defect depends greatly on the family history as a child is more likely to get affected with this misconfiguration if there is a previous history of this defect in the family. Moreover, a child with autosomal dominant genes with reduced penetrance and variable expressions often shows this misconfiguration.
Associated Conditions
- Acrosyndactyly
In this misconfiguration the skin is united for the most part of the finger, however, there is a gap in the syndactyly with normal skin at the proximal area. For eg constriction ring syndrome is a type of acrosyndactyly.
It can be easily diagnosed using clinical therapy and medications.
- Poland Syndrome
Poland syndrome is a condition in which people are born with missing or underdeveloped muscles on one side of their bodies, causing anomalies in the chest, shoulder, arm, and hand. The level and severity of the anomalies varies from person to person.
Part of one of the primary chest muscles, the pectoralis major, is usually missing in people with Poland syndrome. In minor cases medication and therapy can cure the syndrome but in severe cases surgery is the only way out.
- Apert Syndrome
Apert syndrome is a skeletal condition caused by a genetic mutation. The premature closure of the skull bones is a fundamental aspect of Apert syndrome. The skull is unable to grow normally as a result of this early fusion, which alters the contour of the head and face. A diverse number of fingers and toes are also fused together (syndactyly). Many people with Apert syndrome suffer vision impairments as a result of eye abnormalities such as bulging eyes, wide-set eyes, and other related symptoms.
Apparently, this syndrome is lifelong and no perfect cure has been discovered yet but still there are surgeries through which the pressure on the brain can significantly decrease to give relief to your child.
Other associated conditions like Carpenter syndrome leads to acrocephalopolysyndactyly which is highly undesirable.
Classification Of The Syndactyly
- Simple: Fingers are joined via skins and tissue only and it is very easy to operate
- Complex: It is similar to simple syndactyly but epithelial bones are also connected which makes it difficult to operate.
- Complicated: It is rare and perhaps the most severe form of syndactyly in which there is abnormal production of bones and tendons.
Treatment For Syndactyly
The operation method of Digital release is adopted to treat syndactyly. It follows the procedure to perform operations on one finger at a time to avoid compromising vasculature.
Moreover, the digits with significant length differences are done first to avoid growth differences. Border digits (ring and thumb-index) are released earliest (at 6 months) because of differences in growth rates between ring-little and thumb-index digits.Because middle and ring digits grow at similar rates, middle-ring syndactyly can be released later (2 years old). If syndactyly involves index-middle-ring-small digits, release index-middle and ring-small first, and leave the central syndactyly (middle-ring) for 6 months later.
It is advised to complete all the procedures of the operation before your child reaches the schooling age.
Complications Of This Operation
Every operation has its own set of complications, web creep is a significant problem that is associated with operation of syndactyly. It is a most common complication related this operation which is caused by necrosis of the tip of the dorsal quadrilateral flap and loss of full-thickness skin graft placed in the web in the early stages of creep, in the later stages(late creep) it is caused by discrepant growth between scar/skin graft and surrounding tissue during the growth spurt.
Currently the treatment to deal with web creep is reconstruction of web space with local skin flaps.